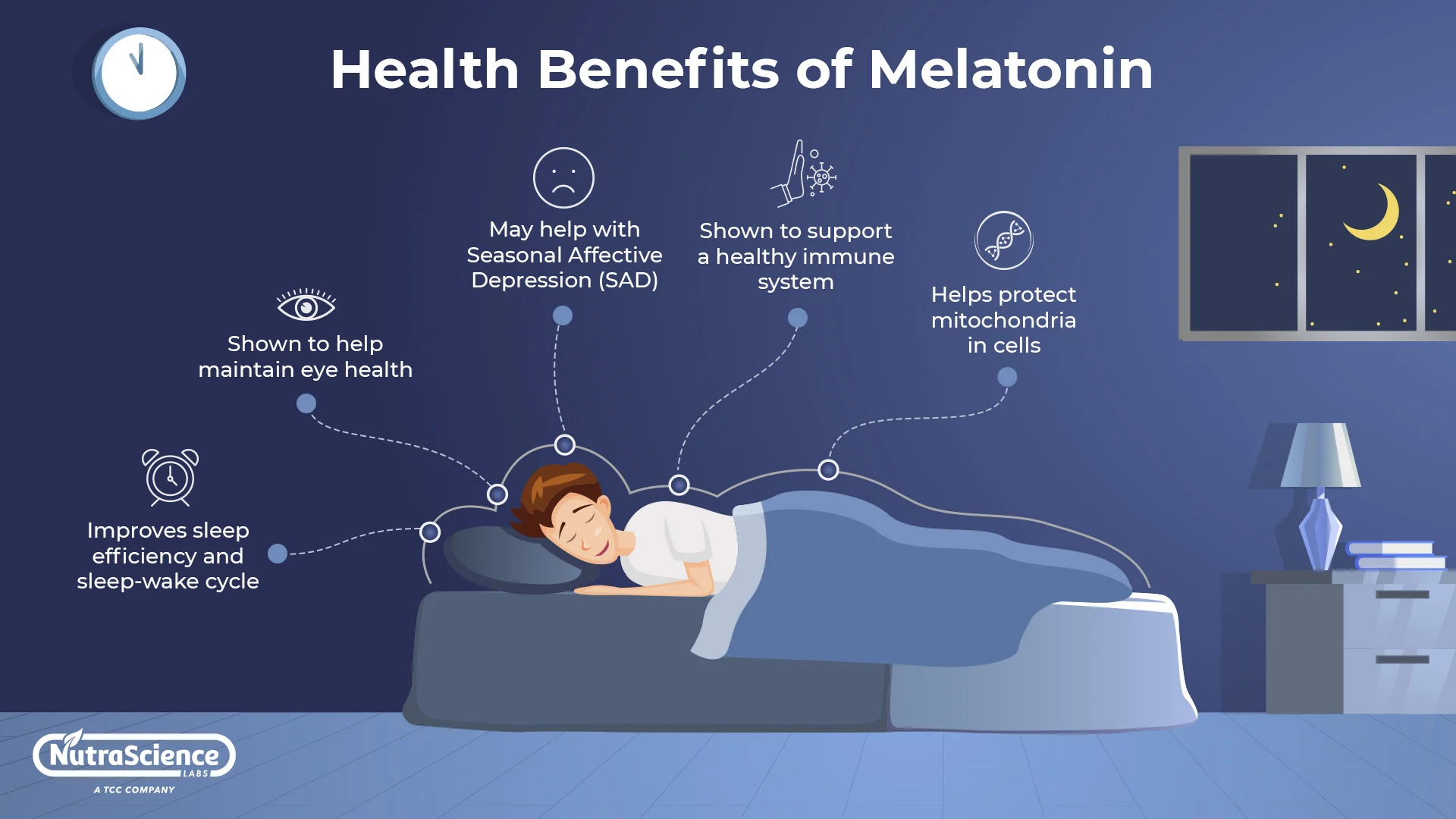
Introduction
Melatonin is a hormone produced naturally by the body that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles. It is commonly known as the “sleep hormone” because of its association with promoting sleep and adjusting circadian rhythms. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the effects of melatonin on sleep and delve into its mechanisms of action. We will discuss the role of melatonin in sleep regulation, its impact on sleep quality and quantity, and the potential benefits and considerations of using melatonin supplements to improve sleep. By understanding how melatonin affects sleep, you can make informed decisions about its use and better optimize your sleep-wake patterns.
Section 1: The Role of Melatonin in Sleep Regulation
1.1 Circadian Rhythms: Explain the concept of circadian rhythms and their influence on sleep-wake cycles. Discuss how melatonin production is regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the brain and its relationship to the sleep-wake cycle.
1.2 Melatonin Synthesis and Release: Describe the process of melatonin synthesis in the pineal gland and its release into the bloodstream. Discuss how melatonin levels rise in the evening, signaling the onset of sleep, and decline in the morning, promoting wakefulness.
Section 2: Melatonin and Sleep Quality
2.1 Sleep Onset: Explore how melatonin promotes sleep onset by signaling the body to prepare for sleep. Discuss its role in reducing sleep latency, or the time it takes to fall asleep, and how melatonin can be helpful for individuals with insomnia or delayed sleep phase disorder.
2.2 Sleep Maintenance: Discuss how melatonin can help regulate sleep patterns and reduce nighttime awakenings. Explain its role in promoting sleep continuity and reducing sleep fragmentation, leading to improved sleep quality.
2.3 Sleep Architecture: Explain the influence of melatonin on sleep architecture, including the distribution of sleep stages. Discuss its impact on rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and slow-wave sleep (SWS), and how melatonin can support the maintenance of a healthy sleep cycle.
Section 3: External Factors Affecting Melatonin Production
3.1 Light Exposure: Discuss the impact of light exposure, particularly blue light emitted by electronic devices, on melatonin production. Explain how exposure to bright light in the evening can suppress melatonin levels, delaying sleep onset and disrupting sleep patterns.
3.2 Shift Work and Jet Lag: Explore how disruptions in the natural light-dark cycle, such as shift work or travel across time zones, can affect melatonin production and sleep-wake patterns. Discuss the potential use of melatonin supplements to help regulate sleep in these situations.
Section 4: Using Melatonin Supplements for Sleep
4.1 Benefits of Melatonin Supplements: Discuss the potential benefits of using melatonin supplements for sleep, including addressing jet lag, managing shift work-related sleep disturbances, and improving sleep quality for individuals with certain sleep disorders.
4.2 Considerations and Precautions: Highlight the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before starting melatonin supplementation, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or taking other medications. Discuss the appropriate dosage and timing of melatonin supplements.
4.3 Safety and Side Effects: Explain the general safety profile of melatonin and the potential side effects, such as daytime drowsiness, headache, or gastrointestinal symptoms. Discuss the importance of using melatonin supplements responsibly and avoiding long-term dependency.
Section 5: Promoting Natural Melatonin Production
5.1 Sleep-Enhancing Lifestyle Habits: Provide tips for promoting natural melatonin production through lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment
5.1 Sleep-Enhancing Lifestyle Habits: Provide tips for promoting natural melatonin production through lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene. Discuss the importance of managing stress and incorporating relaxation techniques to support healthy melatonin production.
5.2 Light Management: Provide strategies for managing light exposure to support melatonin production. Discuss the importance of limiting exposure to bright lights, particularly in the evening, and the use of blue light filters on electronic devices to minimize the suppression of melatonin.
5.3 Dietary Considerations: Discuss how certain foods can influence melatonin production. Highlight foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey, nuts, and seeds, that can support the synthesis of melatonin. Discuss the potential benefits of incorporating a balanced diet and avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime.
Conclusion
Melatonin plays a vital role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and promoting restful sleep. Understanding how melatonin affects sleep can help individuals optimize their sleep patterns and improve sleep quality. Melatonin supplementation can be beneficial for specific sleep-related conditions, such as insomnia, jet lag, or shift work, when used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
However, it is important to prioritize natural melatonin production by adopting healthy sleep habits, managing light exposure, and incorporating sleep-enhancing lifestyle practices. By maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene, individuals can support their body’s natural production of melatonin.
It is essential to recognize that melatonin is not a cure-all for sleep issues and that individual responses may vary. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking medications. Additionally, it is important to use melatonin supplements responsibly and avoid long-term dependency.
By combining knowledge of melatonin’s role in sleep regulation with healthy lifestyle practices, individuals can optimize their sleep-wake patterns, improve sleep quality, and experience the benefits of restorative and rejuvenating sleep. Prioritizing sleep and supporting the body’s natural melatonin production can contribute to overall well-being and enhance one’s quality of life.
- Melo THC Seltzers: A Fun and Refreshing Review of Grapefruit and Wild Berries Flavors - May 14, 2024
- CBD OIL By Swdistro-The Ultimate CBD Oil Comprehensive Analysis and Review - March 29, 2024
- CBD Bath Bombs By Just CBD-Savoring Serenity: My Journey with JustCBD’s Luxurious CBD Bath Products - March 11, 2024